Explain the Difference Between Catabolism and Anabolism
The model that helps explain how an enzyme works is the A activation model. What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism.
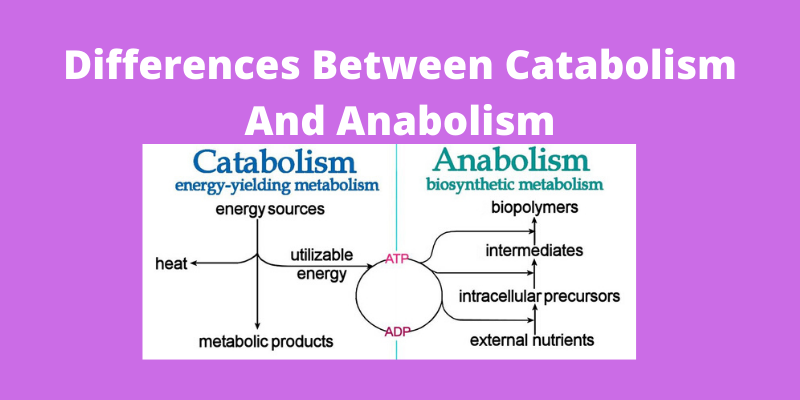
Differences Between Catabolism And Anabolism In Human Body
Respiration is the process in which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment.
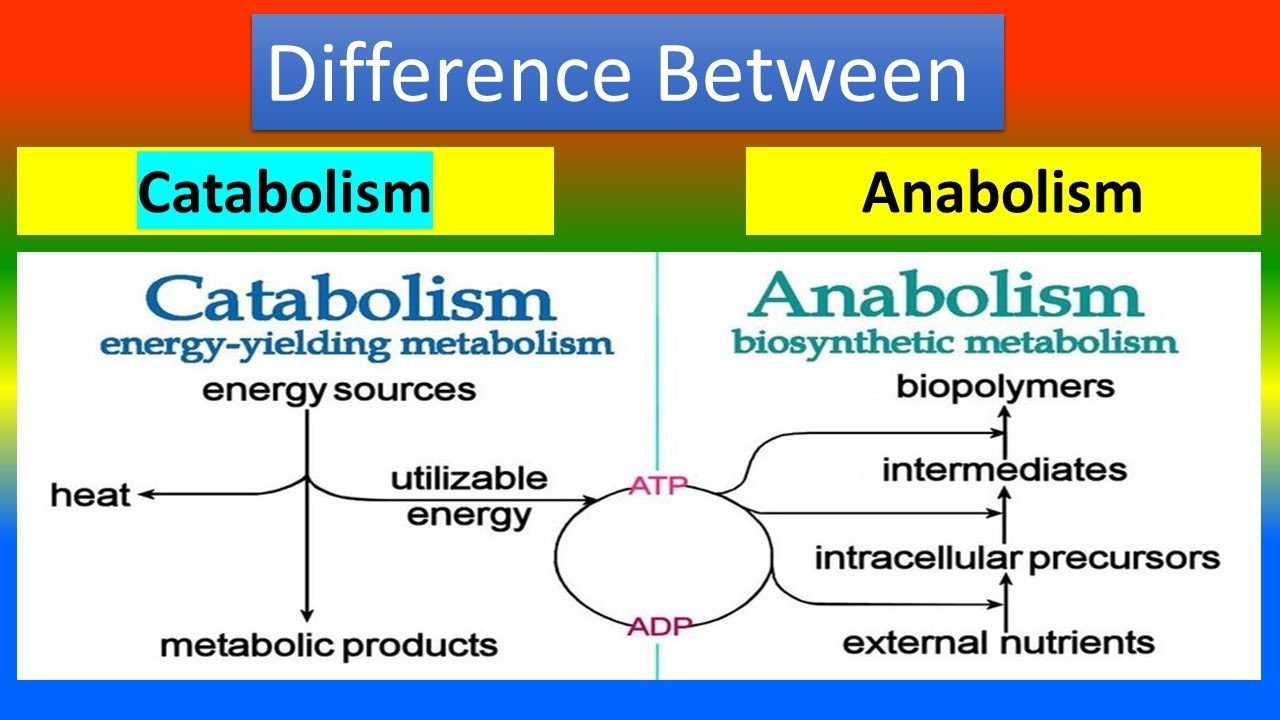
. Explain how atoms form molecules and compounds and describe the nature of the various types of bonds that join them. E have nothing to. B hold the nucleus together.
Catabolism is the degradation of complex macromolecules into simpler molecules such as carbon dioxide water and ammonia. Accordingly we use the conceptual. _____ _____ Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action In 1894 scientist Emil Fisher wrote To use a picture I would like to say that enzyme and glucoside have to fit to each other like a lock and key in order to exert a chemical effect on each other Fisher created a.
C are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Citation needed The largest difference in muscle fiber size between AAS users and non-users was observed in type I muscle fibers of the vastus lateralis and the trapezius muscle as a result of long-term AAS self-administration. Since the respiratory pathway is responsible for both catabolism and anabolism it is known as the amphibolic pathway.
Notes About the Reactions. You cannot tell how quickly a reaction will occur based on whether it is endergonic or exergonic. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because.
D are proteins that function as enzymes. These chemical reactions comprise both the synthesis and degradation of complex macromolecules and can be divided into either catabolism or anabolism Figure 1 catabolism vs anabolism. Both protein anabolism and catabolism increase after exercise but the increase in anabolism is relatively larger causing the net muscle protein balance to be positive.
Takes in energy and is always non spontaneous. First respiration may refer to external respiration or the process. Nucleotides A are part of DNA molecules but not RNA molecules.
From prokaryotic bacteria and archaeans to eukaryotic protists fungi plants and animals all living organisms undergo respirationRespiration may refer to any of the three elements of the process. View Answer For the following energy system list the macronutrients being utilized. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products.
Describe the difference between metabolism catabolism and anabolism. In his experiment Phillips et al. Releases energy and is always spontaneous.
Explain why the above process is an example of anabolism. The participants in the study were allowed to consume meals prior. The root word bio means life so biosynthesis is the process of new substances developing within the body and may also be called anabolism or biogenesis.
Monomers -- polymers What is the difference between an exergonic and endergonic reaction. Substances are withdrawn from the respiratory pathway during the synthesis of fats and proteins and are used in anabolism. A anabolism b catabolism c metabolism d catalysis e homeostasis Answer.
SO 222 Distinguish among ionic. Formation of substances is called anabolism and breakdown of substances is known as catabolism. SO 221 Describe how valence electrons form chemical bonds.
After drug withdrawal the effects fade away slowly but may persist for more than 612 weeks after cessation of AAS use. 6 used 8 sets of 8 concentric and eccentric muscle actions at 80 of each subjects single repetition maximum effort. Polymers -- monomers Anabolism.
Easy Study Objective 1. Here we define two pathwaysex vivo modification and in vivo turnoverwhich jointly explain soil C dynamics driven by microbial catabolism andor anabolism. Anabolism is the biosynthetic pathways that.
Explain the difference between catalysis and catabolism. Catalysts may be needed to cause the reaction to proceed at an observable rate. For example rust formation oxidation of iron is an exergonic and exothermic reaction yet it proceeds so slowly its difficult to notice the release of heat to the.
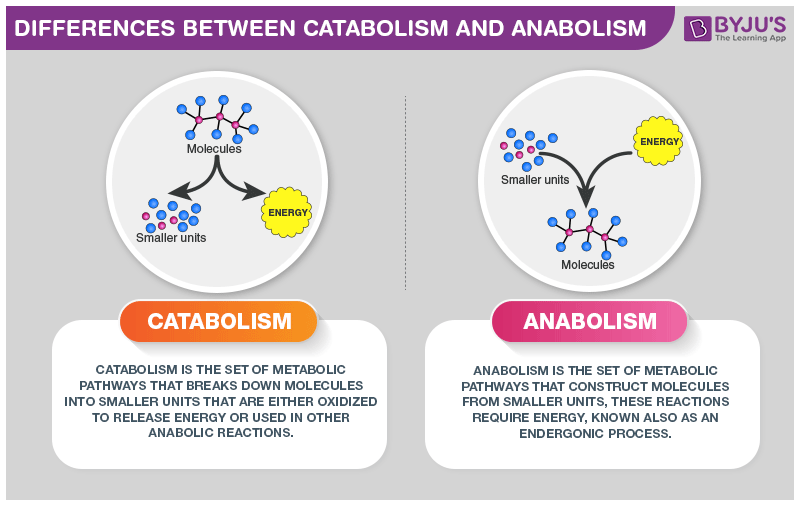
Differences Between Catabolism And Anabolism
Difference Between Anabolism And Catabolism Definition Processes Stages Comparison
No comments for "Explain the Difference Between Catabolism and Anabolism"
Post a Comment